Key Terms:
Zero-day | A recently discovered security vulnerability in computer software that has no currently available fix or patch. Its name come from the reality that vendors have “zero days” to act and respond.
N-day | A vulnerability that emerges in computer software in which a vendor is aware and may have already issued (or are currently working on) a patch or fix. Active exploits often already exist and await abuse by nefarious actors.
Traditional security solutions often apply signature-based-detection when identifying cyber threats, helping to defend against legacy attacks but consequently missing novel ones. Therefore, security teams often lend a lot of focus to ensuring that the risk of zero-day vulnerabilities is reduced [1]. As explored in this blog, however, organizations can face just as much of a risk from n-day attacks, since they invite the most attention from malicious actors [2]. This is due in part to the reduced complexity, cost and time invested in researching and finding new exploits compared with that found when attackers exploit zero-days.
This blog will examine both a zero-day and n-day attack that two different Darktrace customers faced in the fall of 2021. This will include the activity Darktrace detected, along with the steps taken by Darktrace/Network to intervene. It will then compare the incidents, discuss the possible dangers of third-party integrations, and assess the deprecation of legacy security tools.
Revisiting zero-day attacks
Zero-days are among the greatest concerns security teams face in the era of modern technology and networking. Defending critical systems from zero-day compromises is a task most legacy security solutions are often unable to handle. Due to the complexity of uncovering new security flaws and developing elaborate code that can exploit them, these attacks are often carried out by funded or experienced groups such as nation-state actors and APTs. One of history’s most prolific zero-days, ‘Stuxnet’, sent security teams worldwide into a global panic in 2010. This involved a widespread attack on Iranian nuclear infrastructure and was widely accepted to be a result of nation-state actors [3]. The Stuxnet worm took advantage of four zero-day exploits, compromising over 200,000 devices and physically damaging around 10% of the 9,000 critical centrifuges at the Natanz nuclear site.
More recently, 2021 saw the emergence of several critical zero-day vulnerabilities within SonicWall’s product suite [4]. SonicWall is a security hardware manufacturer that provides hardware firewall devices, unified threat management, VPN gateways and network security solutions. Some of these vulnerabilities lie within their Secure Mobile Access (SMA) 100 series (for example, CVE-2019-7481, CVE-2021-20016 and CVE-2021-20038 to name a few). These directly affected VPN devices and often allowed attackers easy remote access to company devices. CVE-2021-20016 in particular incorporates an SQL-Injection vulnerability within SonicWall’s SSL VPN SMA 100 product line [5]. If exploited, this defect would allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to perform their own malicious SQL query in order to access usernames, passwords and other session related information.
The N-day underdog
The shadow cast by zero-day attacks often shrouds that of n-day attacks. N-days, however, often pose an equal - if not greater - risk to the majority of organizations, particularly those in industrial sectors. Since these vulnerabilities have fixes available, all of the hard work around research is already done; malicious actors only need to view proof of concepts (POCs) or, if proficient in coding, reverse-engineer software to reveal code-changes (binary diffing) in order to exploit these security flaws in the wild. These vulnerabilities are typically attributed to opportunistic hackers and script-kiddies, where little research or heavy lifting is required.
August 2021 gave rise to a critical vulnerability in Atlassian Confluence servers, namely CVE-2021-26084 [6]. Confluence is a widely used collaboration wiki tool and knowledge-sharing platform. As introduced and discussed a few months ago in a previous Darktrace blog, this vulnerability allows attackers to remotely execute code on internet-facing servers after exploiting injection vulnerabilities in Object-Graph Navigation Language (OGNL). Whilst Confluence had patches and fixes available to users, attackers still jumped on this opportunity and began scanning the internet for signs of critical devices serving this outdated software [7]. Once identified, they would exploit the vulnerability, often installing crypto mining software onto the device. More recently, Darktrace explored a new vulnerability (CVE-2022-26134), disclosed midway through 2022, that affected Confluence servers and data centers using similar techniques to that found in CVE-2021-26084 [8].
SonicWall in the wild – 1. Zero-day attack
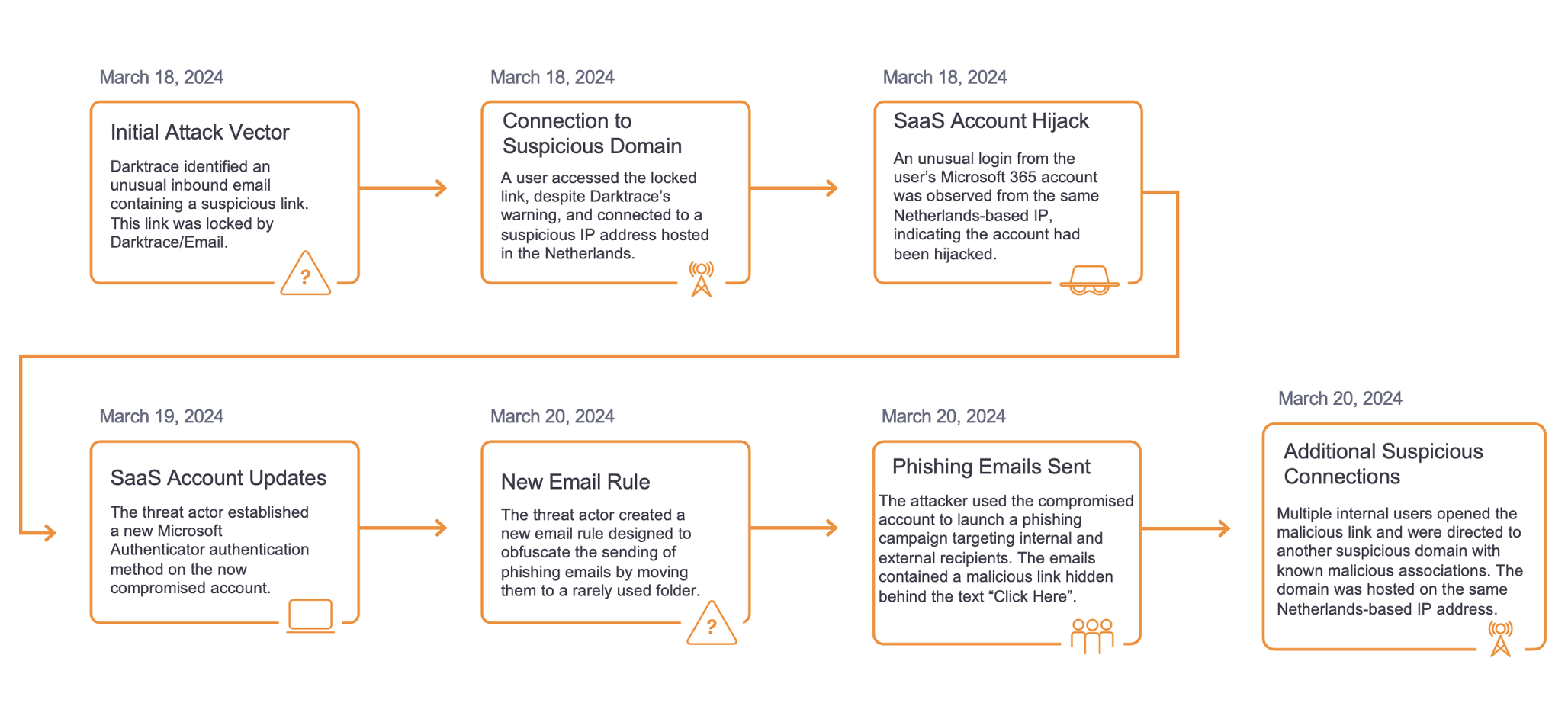
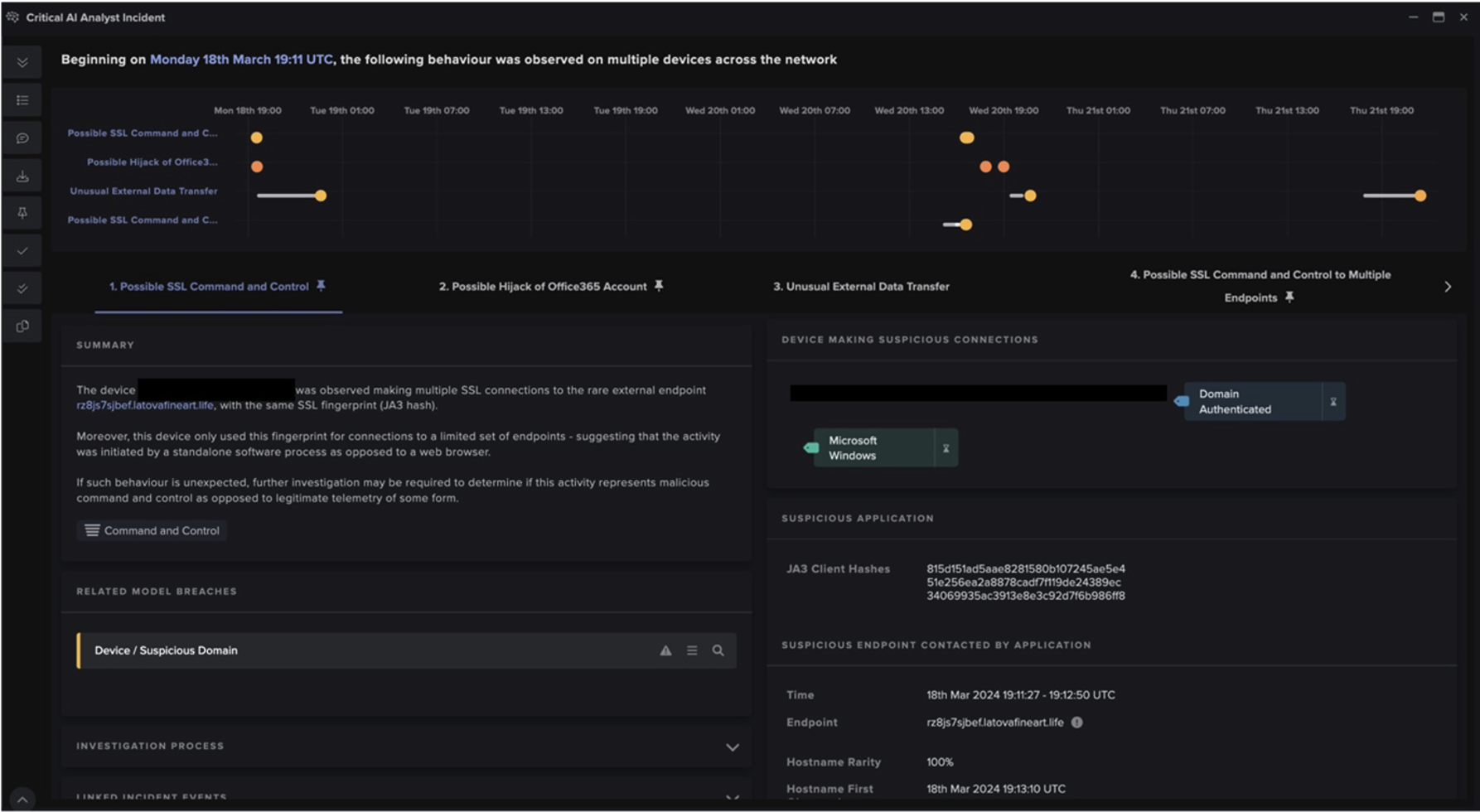
At the beginning of August 2021, Darktrace prevented an attack from taking place within a European automotive customer’s environment (Figure 1). The attack targeted a vulnerable internet-facing SonicWall VPN server, and while the attacker’s motive remains unclear, similar historic events suggest that they intended to perform ransomware encryption or data exfiltration.

Darktrace was unable to confirm the definite tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs) used by the attacker to compromise the customer’s environment, as the device was compromised before Darktrace installation and coverage. However, from looking at recently disclosed SonicWall VPN vulnerabilities and patterns of behaviour, it is likely CVE-2021-20016 played a part. At some point after this initial infection, it is also believed the device was able to move laterally to a domain controller (DC) using administrative credentials; it was this server that then initiated the anomalous activity that Darktrace detected and alerted on.
On August 5th 2021 , Darktrace observed this compromised domain controller engaging in unusual ICMP scanning - a protocol used to discover active devices within an environment and create a map of an organization’s network topology. Shortly after, the infected server began scanning devices for open RDP ports and enumerating SMB shares using unorthodox methods. SMB delete and HTTP requests (over port 445 and 80 respectively) were made for files named delete.me in the root directory of numerous network shares using the user agent Microsoft WebDAV. However, no such files appeared to exist within the environment. This may have been the result of an attacker probing devices in the network in an effort to see their responses and gather information on properties and vulnerabilities they could later exploit.
Soon the infected DC began establishing RDP tunnels back to the VPN server and making requests to an internal DNS server for multiple endpoints relating to exploit kits, likely in an effort to strengthen the attacker’s foothold within the environment. Some of the endpoints requested relate to:
- EternalBlue vulnerability
- Petit Potam NTLM hash attack tool
- Unusual GitHub repositories
- Unusual Python repositories
The DC made outgoing NTLM requests to other internal devices, implying the successful installation of Petit Potam exploitation tools. The server then began performing NTLM reconnaissance, making over 1,000 successful logins under ‘Administrator’ to several other internal devices. Around the same time, the device was also seen making anonymous SMBv1 logins to numerous internal devices, (possibly symptomatic of the attacker probing machines for EternalBlue vulnerabilities).
Interestingly, the device also made numerous failed authentication attempts using a spoofed credential for one of the organization’s security managers. This was likely in an attempt to hide themselves using ‘Living off the Land’ (LotL) techniques. However, whilst the attacker clearly did their research on the company, they failed to acknowledge the typical naming convention used for credentials within the environment. This ultimately backfired and made the compromise more obvious and unusual.
In the morning of the following day, the initially compromised VPN server began conducting further reconnaissance, engaging in similar activity to that observed by the domain controller. Until now, the customer had set Darktrace RESPOND to run in human confirmation mode, meaning interventions were not made autonomously but required confirmation by a member of the internal security team. However, thanks to Proactive Threat Notifications (PTNs) delivered by Darktrace’s dedicated SOC team, the customer was made immediately aware of this unusual behaviour, allowing them to apply manual Darktrace RESPOND blocks to all outgoing connections (Figure 2). This gave the security team enough time to respond and remediate before serious damage could be done.

Confluence in the wild – 2. N-day attack
Towards the end of 2021, Darktrace saw a European broadcasting customer leave an Atlassian Confluence internet-facing server unpatched and vulnerable to crypto-mining malware using CVE-2021-26084. Thanks to Darktrace, this attack was entirely immobilized within only a few hours of the initial infection, protecting the organization from damage (Figure 3).

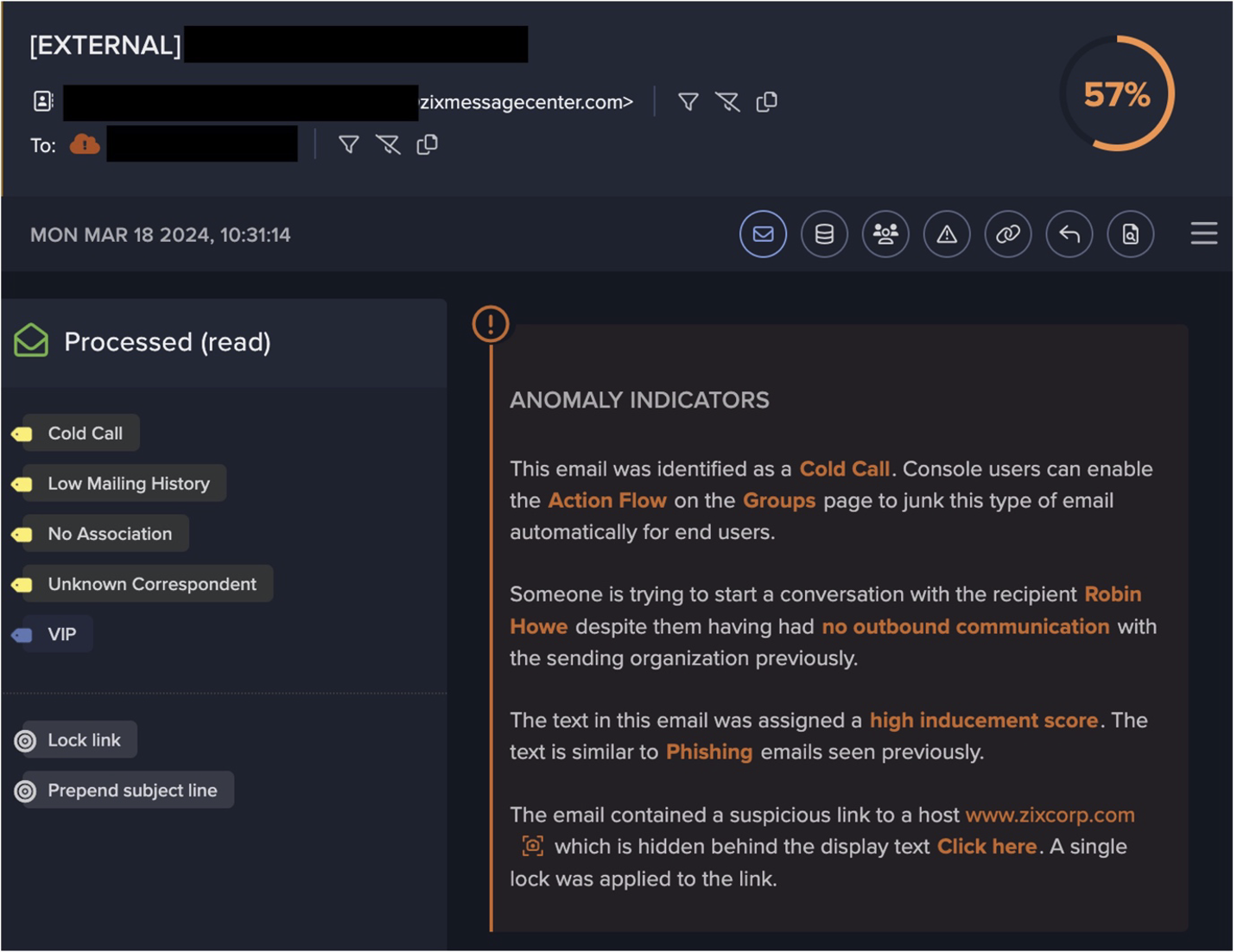
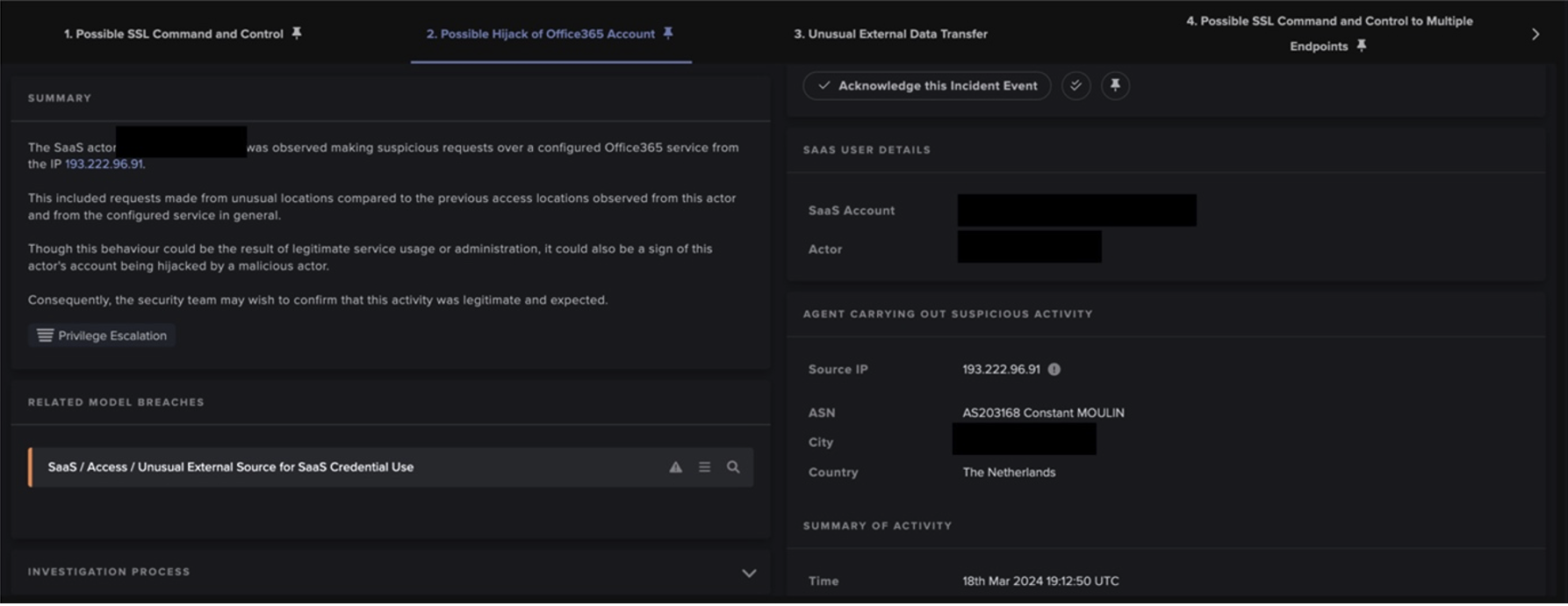
On midday on September 1st 2021, an unpatched Confluence server was seen receiving SSL connections over port 443 from a suspicious new endpoint, 178.238.226[.]127. The connections were encrypted, meaning Darktrace was unable to view the contents and ascertain what requests were being made. However, with the disclosure of CVE-2021-26084 just 7 days prior to this activity, it is likely that the TTPs used involved injecting OGNL expressions to Confluence server memory; allowing the attacker to remotely execute code on the vulnerable server.
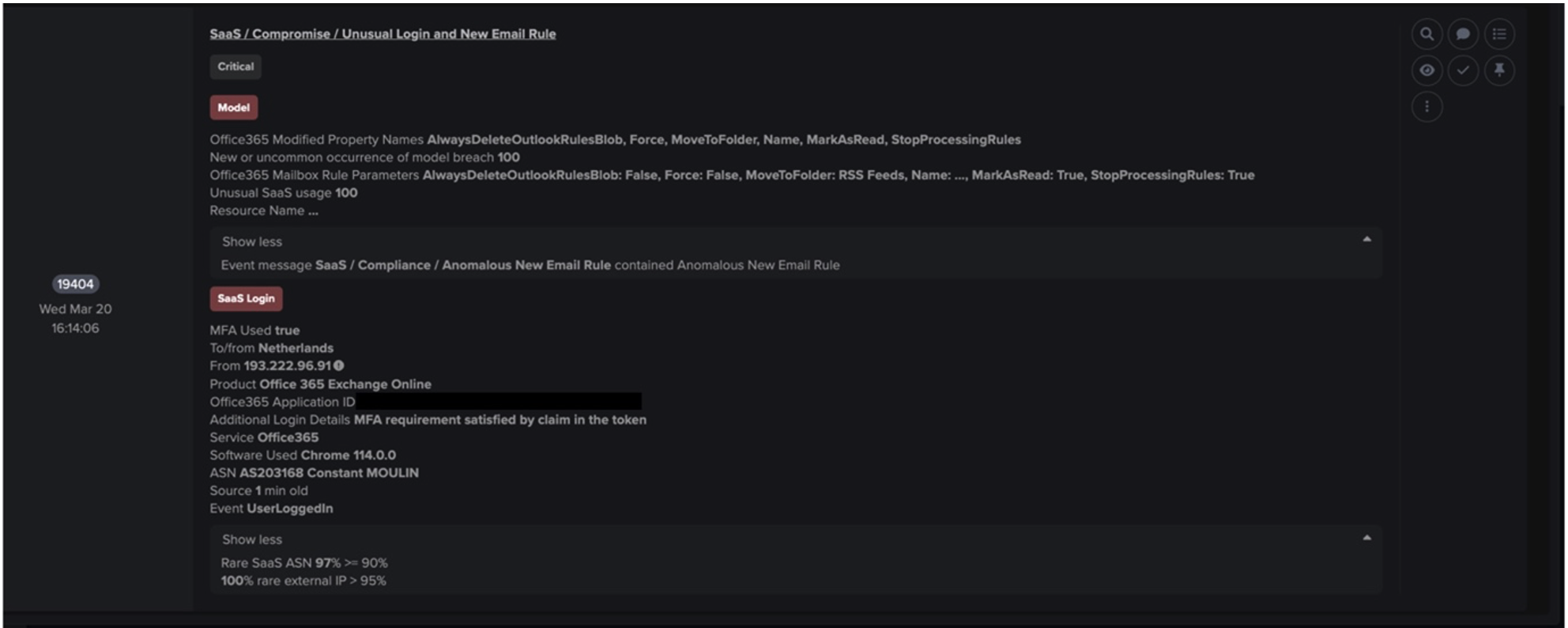
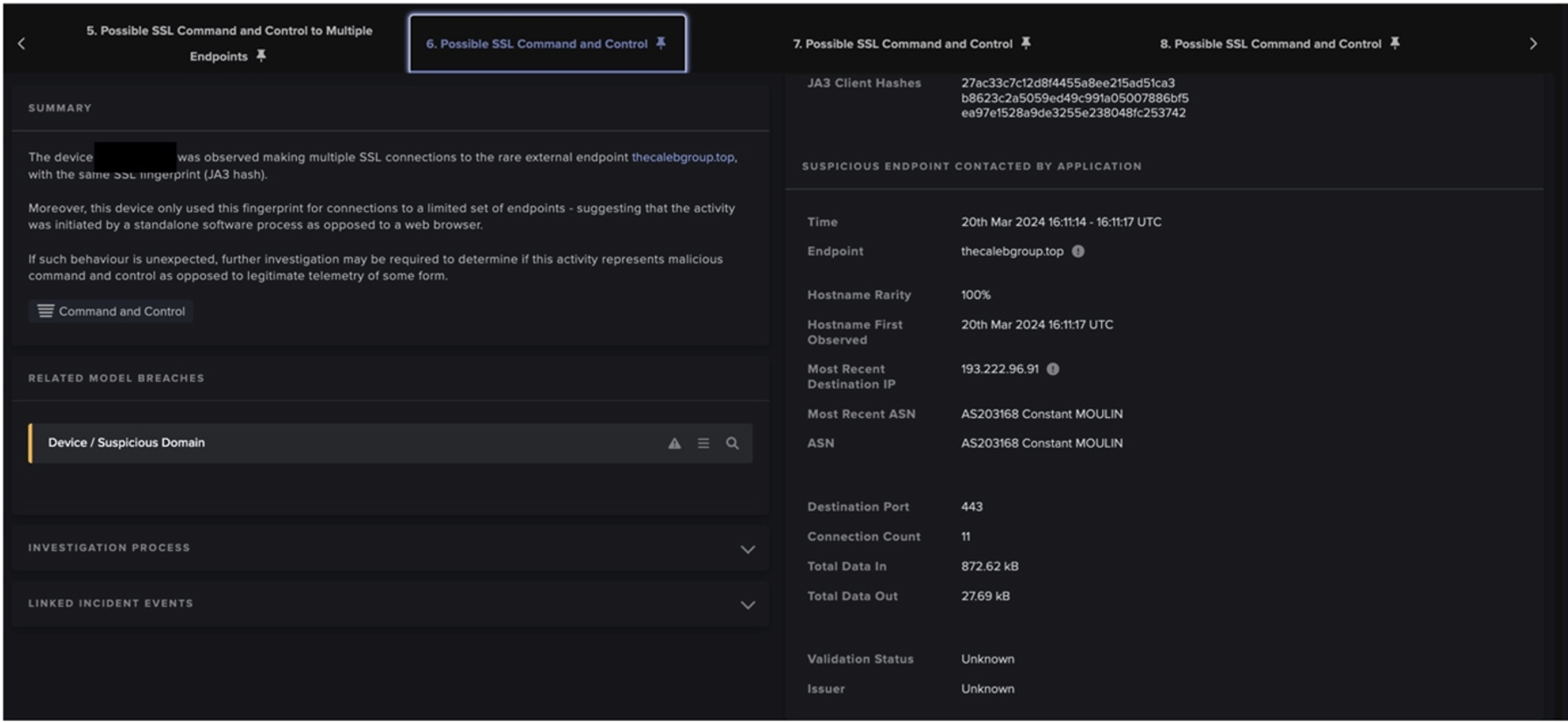
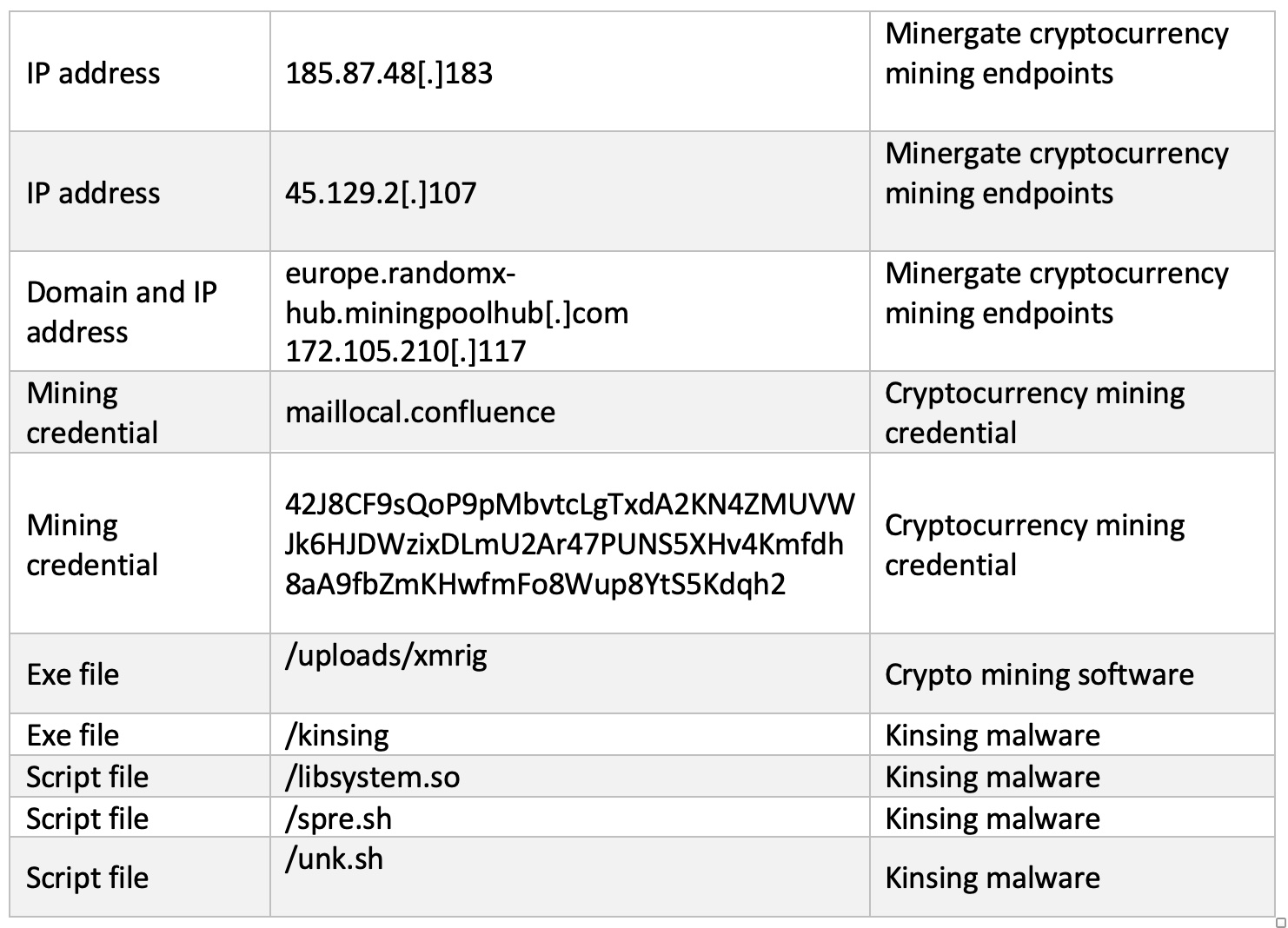
Immediately after successful exploitation of the Confluence server, the infected device was observed making outgoing HTTP GET requests to several external endpoints using a new user agent (curl/7.61.1). Curl was used to silently download and configure multiple suspicious files relating to XMRig cryptocurrency miner, including ld.sh, XMRig and config.json. Subsequent outgoing connections were then made to europe.randomx-hub.miningpoolhub[.]com · 172.105.210[.]117 using the JSON-RPC protocol, seen alongside the mining credential maillocal.confluence (Figure 4). Only 3 seconds after initial compromise, the infected device began attempting to mine cryptocurrency using the Minergate protocol but was instantly and autonomously blocked by Darktrace RESPOND. This prevented the server from abusing system resources and generating profits for the attacker.

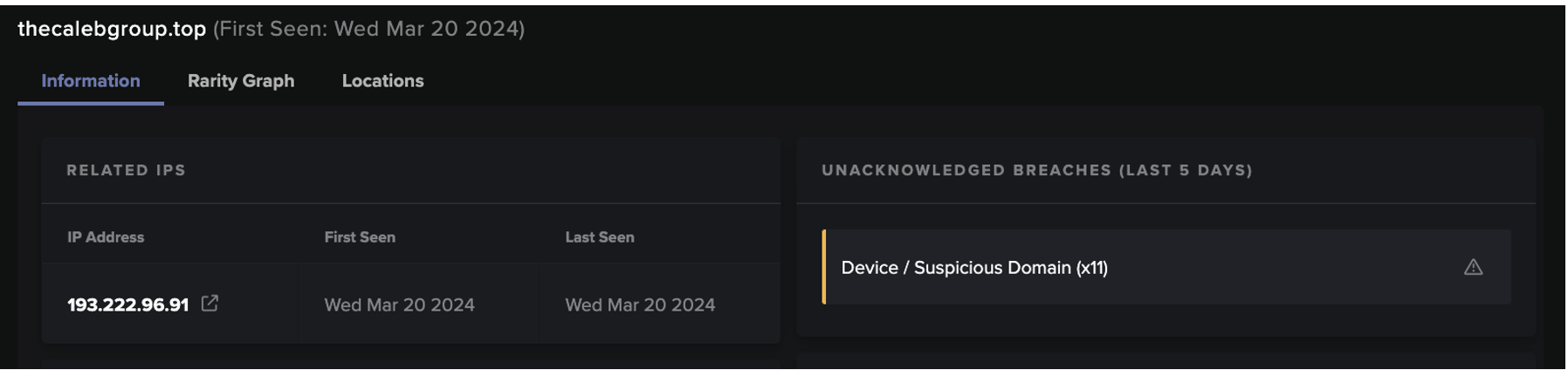
In the afternoon, the malware persisted with its infection. The compromised server began making successive HTTP GET requests to a new rare endpoint 195.19.192[.]28 using the same curl user agent (Figures 5 & 6). These requests were for executable and dynamic library files associated with Kinsing malware (but fortunately were also blocked by Darktrace RESPOND). Kinsing is a malware strain found in numerous attack campaigns which is often associated with crypto-jacking, and has appeared in previous Darktrace blogs [9].

The attacker then began making HTTP POST requests to an IP 185.154.53[.]140, using the same curl user agent; likely a method for the attacker to maintain persistence within the network and establish a foothold using its C2 infrastructure. The Confluence server was then again seen attempting to mine cryptocurrency using the Minergate protocol. It made outgoing JSON-RPC connections to a different new endpoint, 45.129.2[.]107, using the following mining credential: ‘42J8CF9sQoP9pMbvtcLgTxdA2KN4ZMUVWJk6HJDWzixDLmU2Ar47PUNS5XHv4Kmfdh8aA9fbZmKHwfmFo8Wup8YtS5Kdqh2’. This was once again blocked by Darktrace RESPOND (Figure 7).


The final activity seen from this device involved the download of additional shell scripts over HTTP associated with Kinsing, namely spre.sh and unk.sh, from 194.38.20[.]199 and 195.3.146[.]118 respectively (Figure 8). A new user agent (Wget/1.19.5 (linux-gnu)) was used when connecting to the latter endpoint, which also began concurrently initiating repeated connections indicative of C2 beaconing. These scripts help to spread the Kinsing malware laterally within the environment and may have been the attacker's last ditch efforts at furthering their compromise before Darktrace RESPOND blocked all connections from the infected Confluence server [11]. With Darktrace RESPOND's successful actions, the customer’s security team were then able to perform their own response and remediation.

Darktrace Coverage: N- vs Zero-days
In the SonicWall case the attacker was unable to achieve their actions on objectives (thanks to Darktrace's intervention). However, this incident displayed tactics of a more stealthy and sophisticated attacker - they had an exploited machine but waited for the right moment to execute their malicious code and initiate a full compromise. Due to the lack of visibility over attacker motive, it is difficult to deduce what type of actor led to this intrusion. However, with the disclosure of a zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2021-20016) not long before this attack, along with a seemingly dormant initially compromised device, it is highly possible that it was carried out by a sophisticated cyber criminal or gang.
On the other hand, the Confluence case engaged in a slightly more noisy approach; it dropped crypto mining malware on vulnerable devices in the hope that the target’s security team did not maintain visibility over their network or would merely turn a blind eye. The files downloaded and credentials observed alongside the mining activity heavily imply the use of Kinsing malware [11]. Since this vulnerability (CVE-2021-26084) emerged as an n-day attack with likely easily accessible POCs, as well as there being a lack of LotL techniques and the motive being long term monetary gain, it is possible this attack was conducted by a less sophisticated or amateur actor (script-kiddie); one that opportunistically exploits known vulnerabilities in internet-facing devices in order to make a quick profit [12].
Whilst Darktrace RESPOND was enabled in human confirmation mode only during the start of the SonicWall attack, Darktrace’s Cyber AI Analyst still offered invaluable insight into the unusual activity associated with the infected machines during both the Confluence and SonicWall compromises. SOC analysts were able to see these uncharacteristic behaviours and escalate the incident through Darktrace’s PTN and ATE services. Analysts then worked through these tickets with the customers, providing support and guidance and, in the SonicWall case, quickly helping to configure Darktrace RESPOND. In both scenarios, Darktrace RESPOND was able to block abnormal connections and enforce a device’s pattern of life, affording the security team enough time to isolate the infected machines and prevent further threats such as ransomware detonation or data exfiltration.
Concluding thoughts and dangers of third-party integrations
Organizations with internet-facing devices will inevitably suffer opportunistic zero-day and n-day attacks. While little can be done to remove the risk of zero-days entirely, ensuring that organizations keep their systems up to date will at the very least help prevent opportunistic and script-kiddies from exploiting n-day vulnerabilities.
However, it is often not always possible for organizations to keep their systems up to date, especially for those who require continuous availability. This may also pose issues for organizations that rely on, and put their trust in, third party integrations such as those explored in this blog (Confluence and SonicWall), as enforcing secure software is almost entirely out of their hands. Moreover, with the rising prevalence of remote working, it is essential now more than ever that organizations ensure their VPN devices are shielded from external threats, guidance on which has been released by the NSA/CISA [13].
These two case studies have shown that whilst organizations can configure their networks and firewalls to help identify known indicators of compromise (IoC), this ‘rearview mirror’ approach will not account for, or protect against, any new and undisclosed IoCs. With the aid of Self-Learning AI and anomaly detection, Darktrace can detect the slightest deviation from a device’s normal pattern of life and respond autonomously without the need for rules and signatures. This allows for the disruption and prevention of known and novel attacks before irreparable damage is caused- reassuring security teams that their digital estates are secure.
Thanks to Paul Jennings for his contributions to this blog.
Appendices: SonicWall (Zero-day)
Darktrace model detections
· AIA / Suspicious Chain of Administrative Credentials
· Anomalous Connection / Active Remote Desktop Tunnel
· Anomalous Connection / SMB Enumeration
· Anomalous Connection / Unusual Internal Remote Desktop
· Compliance / High Priority Compliance Model Breach
· Compliance / Outgoing NTLM Request from DC
· Device / Anomalous RDP Followed By Multiple Model Breaches
· Device / Anomalous SMB Followed By Multiple Model Breaches
· Device / ICMP Address Scan
· Device / Large Number of Model Breaches
· Device / Large Number of Model Breaches from Critical Network Device
· Device / Multiple Lateral Movement Model Breaches (PTN/Enhanced Monitoring model)
· Device / Network Scan
· Device / Possible SMB/NTLM Reconnaissance
· Device / RDP Scan
· Device / Reverse DNS Sweep
· Device / SMB Session Bruteforce
· Device / Suspicious Network Scan Activity (PTN/Enhanced Monitoring model)
· Unusual Activity / Possible RPC Recon Activity
Darktrace RESPOND (Antigena) actions (as displayed in example)
· Antigena / Network / Manual / Quarantine Device
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques Observed

IoCs

Appendices: Confluence (N-day)
Darktrace model detections
· Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
· Anomalous Connection / Posting HTTP to IP Without Hostname
· Anomalous File / EXE from Rare External Location
· Anomalous File / Script from Rare Location
· Compliance / Crypto Currency Mining Activity
· Compromise / High Priority Crypto Currency Mining (PTN/Enhanced Monitoring model)
· Device / Initial Breach Chain Compromise (PTN/Enhanced Monitoring model)
· Device / Internet Facing Device with High Priority Alert
· Device / New User Agent
Darktrace RESPOND (Antigena) actions (displayed in example)
· Antigena / Network / Compliance / Antigena Crypto Currency Mining Block
· Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena File then New Outbound Block
· Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena Suspicious Activity Block
· Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena Suspicious File Block
· Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Block Enhanced Monitoring
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques Observed

IOCs

References:
[1] https://securitybrief.asia/story/why-preventing-zero-day-attacks-is-crucial-for-businesses
[3] https://www.wired.com/2014/11/countdown-to-zero-day-stuxnet/
[4] https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvekey.cgi?keyword=SonicWall+2021
[5] https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2021-20016
[6] https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2021-26084
[8] https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2022-26134
[9] https://attack.mitre.org/software/S0599/
[10] https://www.virustotal.com/gui/ip-address/195.19.192.28/detection
[11] https://sysdig.com/blog/zoom-into-kinsing-kdevtmpfsi/