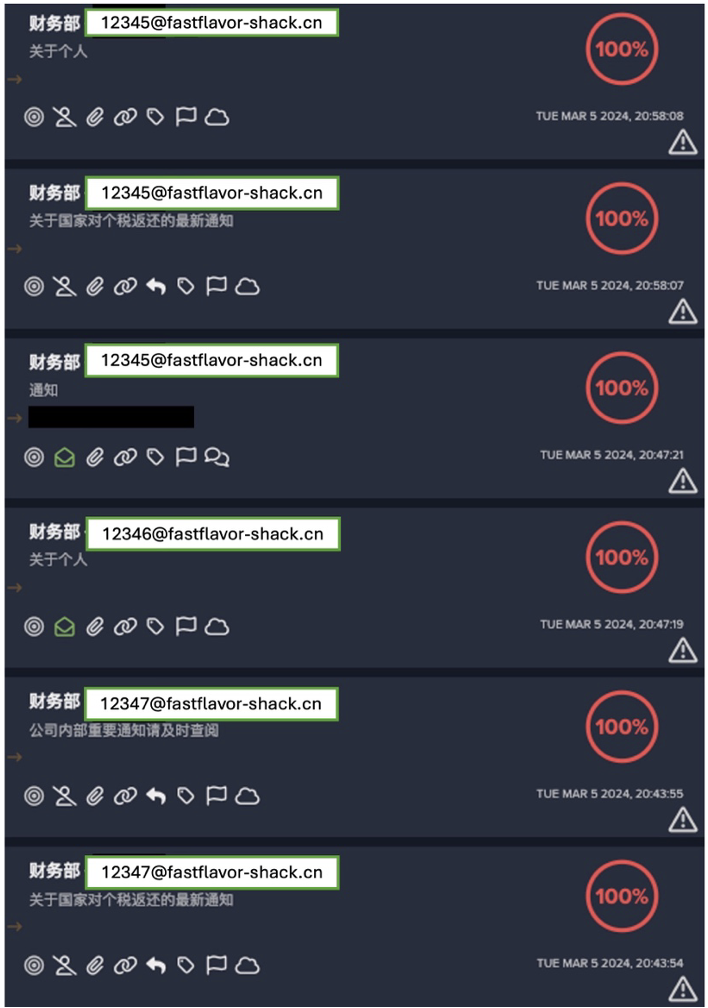
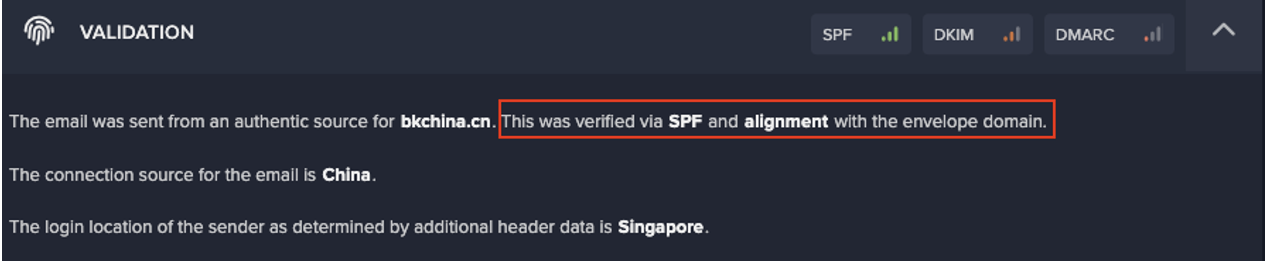
REvil, also known as Sodinokibi, is a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) gang responsible for one of the largest ransomware attacks in history. On 14th January 2022, Russia announced it had arrested 14 members of the criminal gang. The move came at the request of the US authorities, who have worked hard with international partners to crack down on the gang. Last year, multiple high-profile attacks were attributed to the REvil group, including the JBS ransomware and Kaseya supply chain incidents.
The arrests are certainly a victory for western law enforcement agencies, and follows November’s announcement from Europol that seven arrests of REvil affiliates had been made in the preceding months. The question is: to what extent will these arrests disrupt the gang’s operations, and for how long?
Early indications from security researchers at ReversingLabs indicates REvil activity has been unaffected. Statistics on REvil implants two weeks after the Russian arrests are unchanged, and if anything indicate a modest increase.
This continued activity implies one of two scenarios:
- The flurry of arrests have only impacted ‘middle men’ within the criminal gang’s hierarchy
- REvil’s ransomware-as-a-service model is resilient enough to survive disruption from law enforcement
Both scenarios are worrisome to those who may fall prey to ransomware gangs, and the reality is likely to be a far more complex mixture of these and other factors. The crackdown on ransomware is long overdue, but the battle is likely to be a long one. Law enforcement agencies need to disrupt the business model to such an extent that it no longer becomes profitable or favorable to be in the ransomware business, and this is likely to take months or even years.
So as the crackdown on ransomware plays out on the biggest stage, what comfort, if any, can security teams take from recent events?
Staying ahead of the evolving RaaS model with AI
A joint report on ransomware issued recently by the FBI, CISA, the NCSC, the ACSC and the NSA highlighted key trends over the past year:
- RaaS has become increasingly professionalized, with business models and processes now well established.
- The business model complicates attribution because there are complex networks of developers, affiliates, and freelancers.
- Ransomware groups are sharing victim information with each other, diversifying the threat to targeted organizations.
In summary, the report illuminates how ransomware gangs have become increasingly adaptable when it comes to evading law enforcement and maximizing profit from ransom payments. Multiple groups have faded away, or retired, only to reappear under a different name and with a slightly updated playbook. The tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) differ from victim to victim, largely because attacks are conducted by different ransomware operators and affiliates.
This is troubling for law enforcement bodies trying to crack down on the individuals behind these attacks. When a RaaS group like REvil consists of an amorphous and ever-changing web of associates, making individual arrests is a constant game of catch up, and will be unlikely to bring down the group as a whole.
The same battle is being played out on the scale of individual attack campaigns. Security tools focused on the hallmarks of previously encountered threats are also in a continuous state of catch up: by the time a single attack is detected, fingerprinted, and stored for next time, attackers and their techniques have moved on.
But there is another option available to defenders, who are increasingly turning to Self-Learning AI to stay one step ahead of attackers. By learning its digital surroundings and identifying subtle deviations indicative of an attack, this technology can detect and respond to novel attacks on the first encounter. Below is an example of how Self-Learning AI detected an attack launched by REvil without the use of rules or signatures.
REvil threat find
In the summer of 2021, a REvil affiliate launched an attack against a health and social care organization – a sector that has seen a big increase in cyber-attacks since the start of the global pandemic. While the attack was detected by Darktrace’s AI without using rules or signatures, the security team was not monitoring Darktrace at the time. In the absence of Autonomous Response – which would have taken targeted action to contain the threat – the attack was allowed to progress.
After gaining access to the network via the laptop of a remote worker, the attacker was able to abuse a legitimate remote desktop (RDP) connection to a corporate jump server to bruteforce additional credentials.
Once equipped with more credentials, the attacker connected to multiple internal devices via RDP, including a second jump server. Data exfiltration began from the initially compromised server over RDP port 3389.
Two weeks later, the attacker identified the organization’s crown jewels, stored on a third server, and attempted to initiate command and control (C2) communications. The server made a number of unusual external connections, including attempts to connect to a rare domain that resembled the pattern of activity associated with REvil’s earlier Kaseya ransomware campaign.
Darktrace for Endpoint, which was running on remote user devices, provided additional visibility, enabling the security team to determine the initially compromised user device. Had Antigena been active on the endpoint, it would have intervened to stop this unusual activity by blocking the specific unusual connections – containing the attack without impacting normal business operations.
Connecting the dots of a low-and-slow attack
The total dwell time of the attacker was 22 days. They were patient, and undertook actions in bursts of activity often with days in between. This pattern of behavior is not uncommon for ransomware attacks, particularly those using the RaaS model in which each step may be performed by different gang members or affiliates.
Darktrace’s Cyber AI Analyst was able to track in real time the complete attack lifecycle over several weeks, stitching together the separate phases of the attack into a coherent security incident.

Figure 1: Cyber AI Analyst reveals the complete attack kill chain
New name, same game
This attack is another case of threat actors living off the land: using legitimate programs and processes that were already in use in the environment to perform malicious activity. This can be very difficult to detect with traditional tools that are based on static use cases and cannot differentiate a legitimate RDP session from a malicious one.
As cyber-criminal groups like REvil continue to defy law enforcement efforts, defenders need to stay ahead with AI technology that learns its environment, adapts as it changes and grows, and responds to threats based on subtle deviations that indicate an emerging attack. Autonomous Response has been adopted by over thousands of organizations across all areas of the digital estate – from email and cloud services to endpoint devices, stopping ransomware attacks early, before encryption is achieved.
Thanks to Darktrace analyst Petal Beharry for her insights on the above threat find.
Technical details
Darktrace model detections:
- Device / RDP Scan
- Device / Bruteforce Activity
- Compliance / Outbound Remote Desktop
- Anomalous Connection / Upload via Remote Desktop
- Anomalous Connection / Download and Upload
- Anomalous Connection / Uncommon 1 GiB Outbound
- Anomalous Connection / Active Remote Desktop Tunnel
- Device / New or Uncommon SMB Named Pipe
- Device / Large Number of Connections to New Endpoints