Founded in 1964, Priefert Manufacturing has grown into one of the largest farm, ranch, and rodeo equipment manufacturers in the world. With a huge range of equipment in locations that span several acres in the US, it is imperative that all our devices can safely communicate in real time.
We recognize that our biggest vulnerability comes from within – from our own employees. With one misstep or oversight, from a neglected software download to an accidental engagement with a phishing email, a threat actor can get inside our systems and potentially disrupt our business.
A lot of our employees are non-technical, and to continue being productive, we have to accept the risk that comes with giving computer system access to users who are unfamiliar with certain technologies and security protocols.
So, we needed another layer of security that went beyond our existing controls: something that could pick up on any malicious activity within our systems, wherever it may arise and however subtle it may be. Security should never hamper productivity, and we needed technology that could intervene in real time, so that we could keep giving our users access to systems, without having to worry so much about a breach.
As we looked into solutions, we decided to install Darktrace’s AI. We were drawn to the fact that it was effective with virtually any type of technology and had the ability to both detect and take autonomous action against attacks.
Stopping ransomware in its tracks
We had only just begun deploying Antigena, Darktrace’s Autonomous Response technology, when it detected and shut down a ransomware attack.
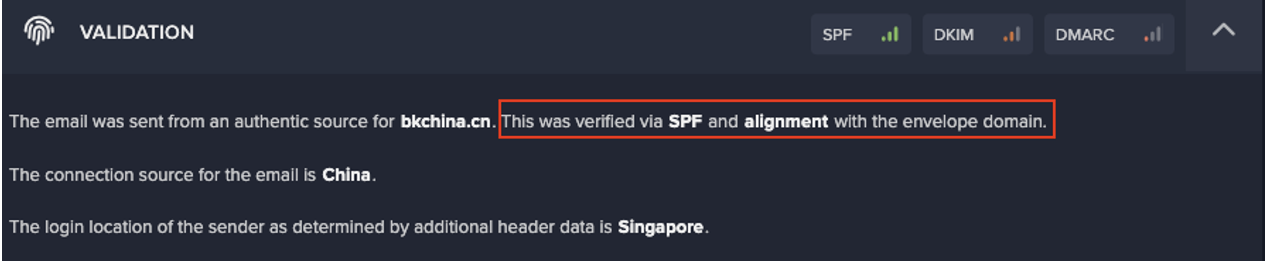
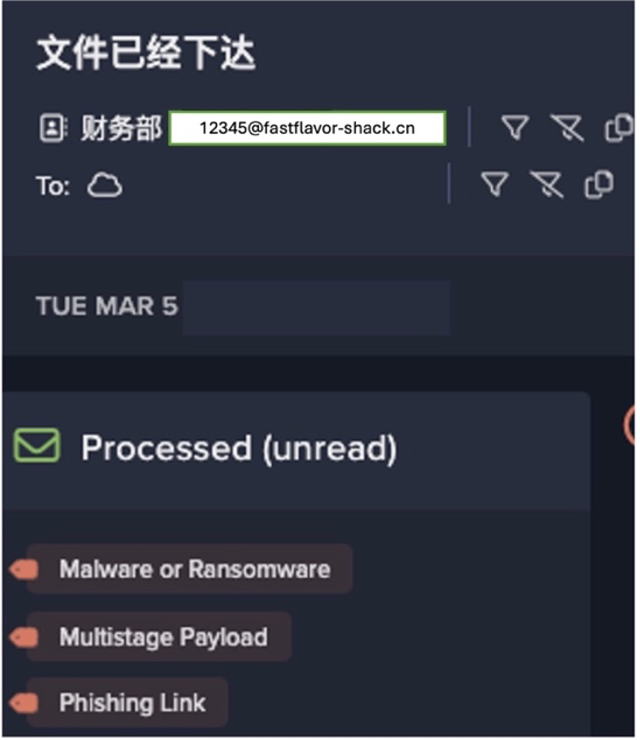
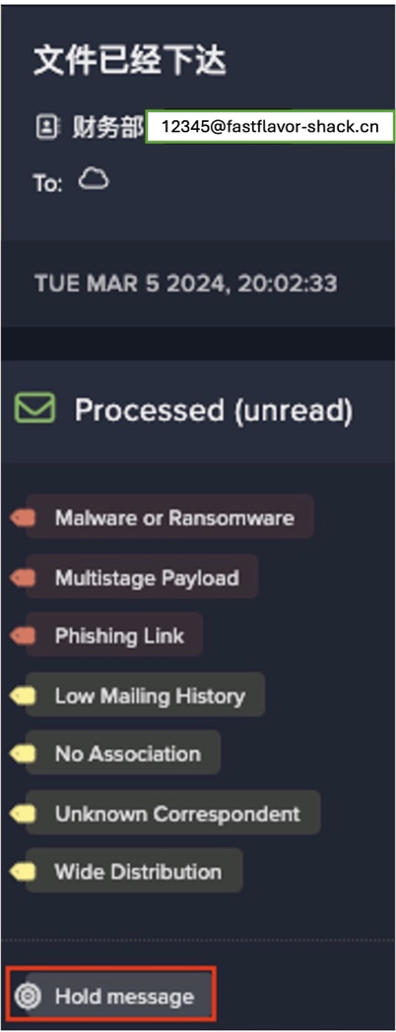
Still in its learning phase, Darktrace was beginning to understand the ‘pattern of life’ across our digital infrastructure when it discovered strange activity on one of our public-facing servers: a series of highly unusual and suspicious connections.
Alerted to the activity, we went ahead and switched Antigena to Active Mode, and we saw the technology in action: it blocked connections to the suspect IP addresses and allowed me to kill the malware on the server, without further spread. Before the ransomware had the chance to create any real damage, Darktrace had shut it down.
We started to understand the full capacity of the technology: not only could it stop in-progress attacks at machine speed, but it was uncovering activity in our network that was previously invisible to us. If we are hit by another similar attack in the future, with Antigena now fully autonomous in our environment, we know that it will take action on its own, responding to any threat in seconds.
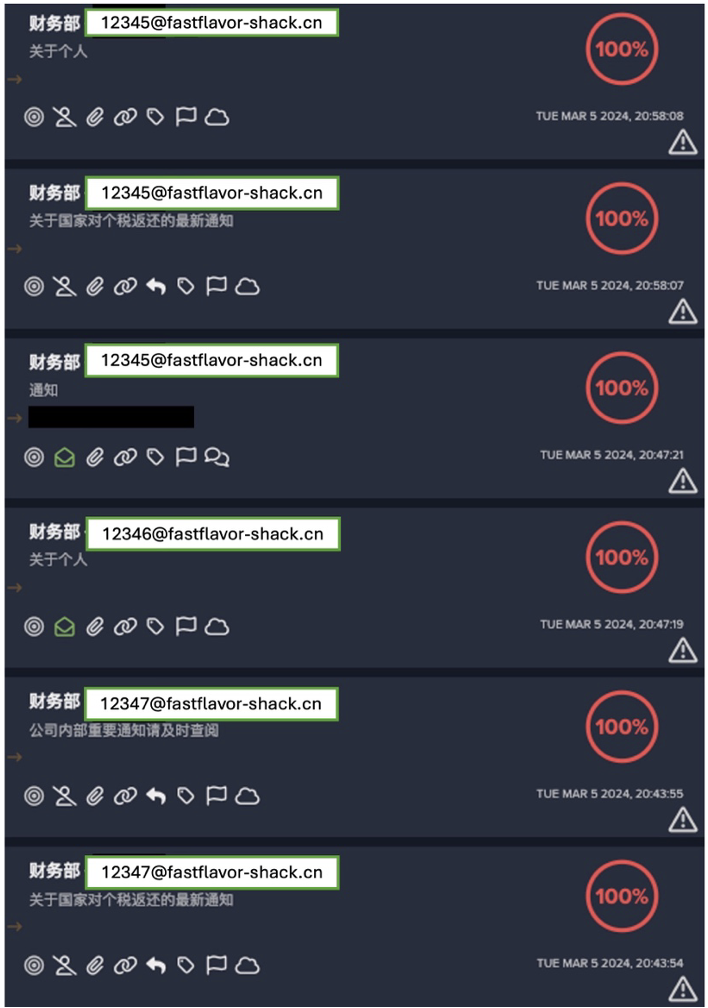
Thwarting phishing attempts
Our experience with Darktrace for SaaS was a similar story. We had just begun rolling out the technology for our Microsoft 365 users when it identified one user account that had been compromised.
At 02:00, a few failed login attempts paired with odd timing prompted Darktrace to flag the account as having unusual user behavior and notify our IT team. Alerted to the situation, we confirmed the account had been hijacked and the threat actor was attempting to send out phishing emails.
Darktrace enabled our team to understand what was going on quickly. With all the information in front of us, we could see that the user did not have multi-factor authentication enabled. They had reused their password for multiple accounts, which meant the attacker was able to get a hold of their credentials. Swiftly, our team attended to the account, halting the outbound emails, and terminating the hacker’s access.
Before Darktrace, we would have never known to activate multi-factor authentication and change the password on this account because we wouldn’t have been aware that the account was exhibiting abnormal behavior in the first place. Previously, until there was a problem, we were left blind to what was going on in our network.
Staying ahead of the threat
As we continue to give our employees more access to new IT systems, we remain confident that Darktrace will neutralize any threat that may arise from a human error before it becomes a crisis. The technology has empowered our team to be proactive instead of reactive – no longer are we reliant on retrospective data and left unaware of a situation until it’s too late.
Without having to go and dig through loads of information, we are notified of potential problems before something or someone in our network presents a problem. We don’t need to wait for any sign of an attack to manifest before we can take action.
The technology has also freed up an extraordinary amount of time for myself, no longer having to focus on manually responding to things that pop up in our systems. I can now spend my time on work I’d like to prioritize, without sacrificing security.
Having a single AI system operate across our entire digital estate – whether it be our network, cloud, or Microsoft 365 users – has only further enhanced the protection Darktrace gives us. It has enabled the technology to absorb huge amounts of data, strengthening its understanding of our environment at the most granular level, so it can pick up on the slightest anomalies indicative of a cyber threat.
And because Darktrace’s AI protects all our digital environments, there are no gaps in protection. Not only can we detect threats that develop in our network, cloud, and email, but we can also now see the full scope of an incident as it progresses across multiple areas of our digital estate. Darktrace shines a light on everything.
Hear more from Darktrace customers